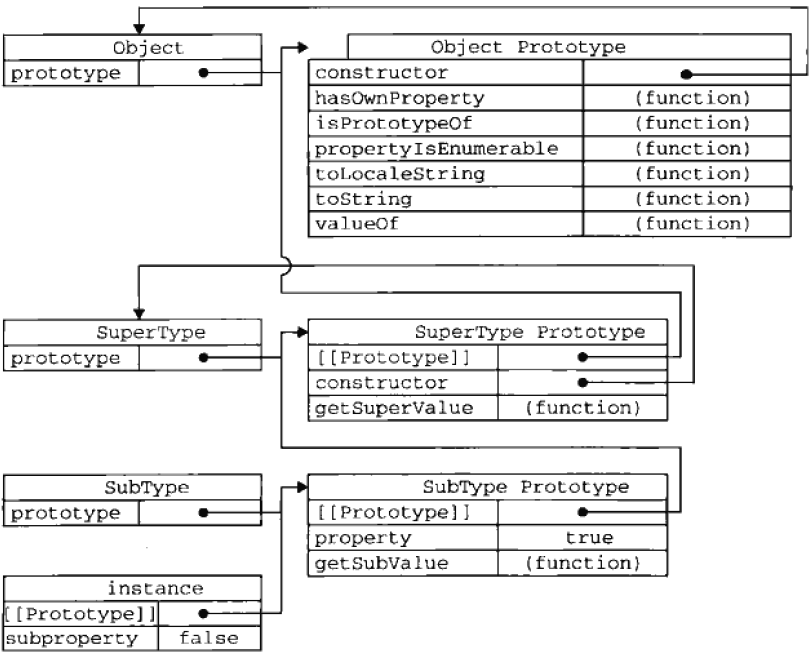
原型链继承 让构造函数的原型对象等于另一个类型的实例,利用原型让一个引用类型继承另一个引用类型的属性和方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 function SuperType() { this.property=true; } SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue=function(){ return this.property; }; function SubType() { this.subProperty=false; } //继承SuperType SubType.prototype=new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.getSubValue=function(){ return this.subProperty; } var instance=new SubType(); alert(instance.getSuperValue());//true
代码示例中,完整原型链如下
原型链继承的问题:父类型引用类型的属性会被所有子类型实例共享,这是不符合预期的
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 function SuperType() { this.colors=["red","blue","green"]; } function SubType() { } //继承SuperType SubType.prototype=new SuperType(); var instance1=new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors);//"red","blue","green","black" var instance2=new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors);//"red","blue","green","black"
借用构造函数继承 基本思想是在子类型构造函数内部调用超类型构造函数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 function SuperType() { this.colors=["red","blue","green"]; } function SubType() { //继承SuperType SuperType.call(this); } var instance1=new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors);//"red","blue","green","black" var instance2=new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors);//"red","blue","green"
借用构造函数可以像超类型构造函数传递参数
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 function SuperType(name) { this.name=name; } function SubType() { //继承SuperType SuperType.call(this,"Jim"); this.age=28; } var instance1=new SubType(); alert(instance1.name);//"Jim" alert(instance1.age);//28
借用构造函数的问题:不能复用超类型的方法
组合继承 使用原型链实现对原型属性和方法的继承,通过借用构造函数实现对实例属性的继承
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 function SuperType(name) { this.name=name; this.colors=["red","blue","green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName=function(){ alert(this.name); }; function SubType(name,age) { //继承SuperType SuperType.call(this,name); this.age=age; } SubType.prototype=new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.sayAge=function(){ alert(this.age); } var instance1=new SubType("Jim",29); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors);//"red","blue","green","black" instance1.sayName();//"Jim" instance1.sayAge();//29 var instance2=new SubType("Jack",28); alert(instance2.colors);//"red","blue","green" instance2.sayName();//"Jack" instance2.sayAge();//28
寄生组合式继承 寄生组合式继承解决了组合继承中,两次调用超类型构造函数的问题
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 function object(o) { function F(){} F.prototype=o; return new F(); } function inheritPrototype(subType,superType) { var prototype =object(superType.prototype); prototype.constructor=superType;//原书是prototype.constructor=subType,看书时认为这里应该是superType subType.prototype=prototype; } function SuperType(name) { this.name=name; this.colors=["red","blue","green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName=function(){ alert(this.name); }; function SubType(name,age) { //继承SuperType SuperType.call(this,name); this.age=age; } inheritPrototype(SubType,SuperType); SubType.prototype.sayAge=function(){ alert(this.age); } var instance1=new SubType("Jim",29); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors);//"red","blue","green","black" instance1.sayName();//"Jim" instance1.sayAge();//29 var instance2=new SubType("Jack",28); alert(instance2.colors);//"red","blue","green" instance2.sayName();//"Jack" instance2.sayAge();//28